[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Centred now on the issue of privacy and whether it is a fundamental right, the hearing of the case regarding Aadhaar in Supreme Court on Thursday saw petitioners cite arguments from international resolutions to argue that right to privacy was implicit in the fundamental rights and also that it was the duty of the state to expand the right rather than curtail it.
Further hearing will continue on Tuesday, July 25.
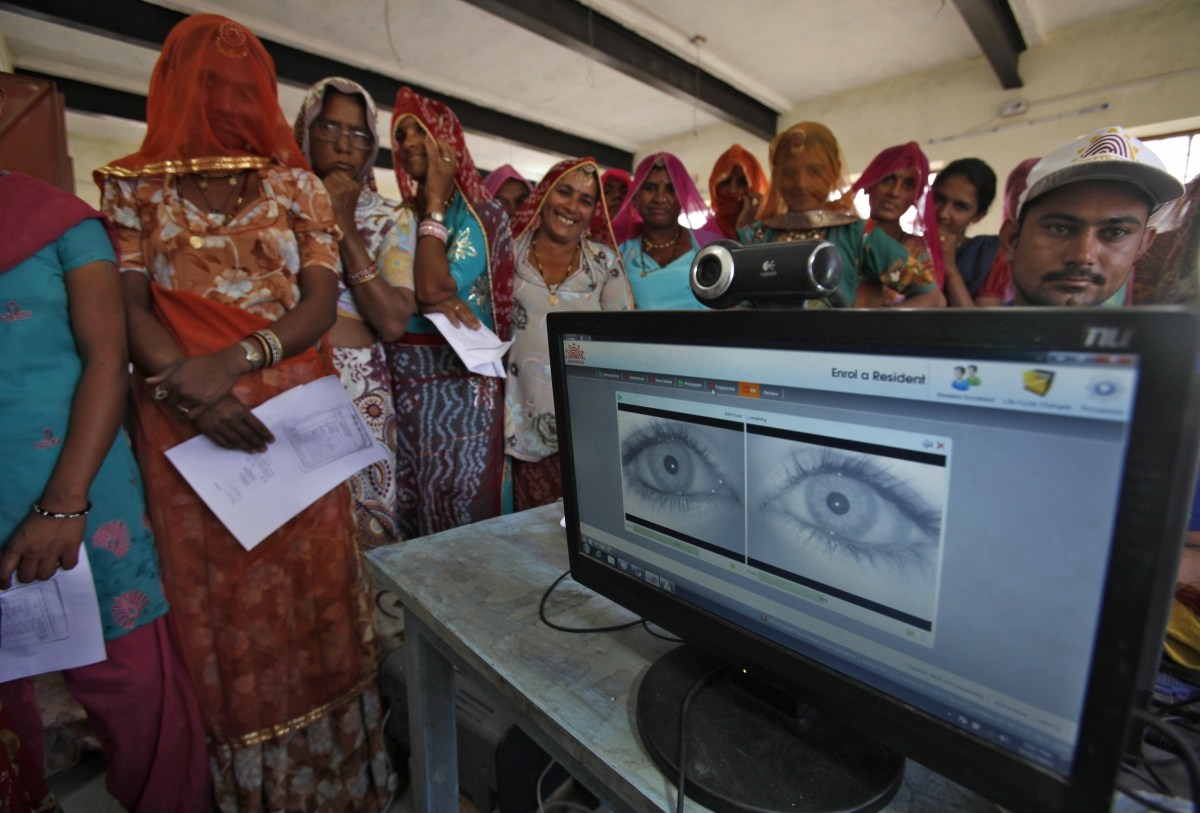
While hearing the case related to Aadhaar and the right to privacy – Aadhaar and its biometric data collection has been challenged as interfering in people’s privacy, and petitions on privacy as a fundamental right are being heard – the special nine-judge constitution bench of the Supreme Court had observed on Wednesday (July 19) that the right to privacy cannot be absolute. It had termed privacy as an amorphous term incorporating several factors.
As the hearings continued on Thursday (July 20), more appellants presented their views on the importance of privacy being incorporated as a fundamental right, even though the Constitution makes no mention of it. It has been said that the writers of the Constitution intentionally omitted privacy as a fundamental right, because of its amorphous nature. However, on Thursday, the arguments were presented also from the international angle where India has been party to several international treaties which spell out privacy as an essential component of basic rights of a human being. Here the argument is if India has acquiesced to agree to this on international forums, how can it deny its own citizens similar rights?
Fifty-five years ago another constitution bench had decided that privacy was not a basic right. This is a larger bench and has the arduous task of deciding whether Indians have the right to retain certain basic information as “private”, or whether the government has the right to tear from its citizens all information even if the citizens concerned are unwilling to reveal the same.
It is not just important to make Aadhaar mandatory for all the functions that the government wants, but also to define the basic rights of a human being in India.
On Wednesday petitioners held up Finance Minister Arun Jaitley’s statement in Parliament when he was moving the Aadhaar Bill in March, saying: “Is privacy a fundamental right or not? The present Bill presupposes and is based on a premise, and it’s too late in the day to contest that privacy is not a fundamental right. Privacy is not an absolute right, which is subjected to a restriction established by law on a fair and just procedure.”
Since it pertains to the Aadhaar bill itself, Jaitley’s statement was not out of context.
The government’s stand, however, was standoffish. Former Attorney General Mukul Rohatgi, while arguing in court, had repeatedly said that Indian citizens donot have a fundamental right to privacy under the Constitution. He was justifying the collection of data such as iris scans and fingerprints taken.
Another important statement was made on Wednesday by senior lawyer Gopal Subramanium, representing the petitioners. He argued that the rights to life and liberty are pre-existing natural rights. “Privacy is embedded in both liberty and dignity. It is not a twilight right but the heart and soul of the Constitution,” he had said.
Also important was the observation of Justice J Chelameswar, a judge on the current bench. He said: “Even freedom of press is not explicit in the constitution but courts have interpreted that the right to free speech includes freedom of expression of press.”
A political interlude had been provided last morning by CPM’s Sitaram Yechury, who had tweeted: “We have a government which believes in the right to privacy for top loan defaulters from being named, but not in Privacy for ordinary citizens. Right to Privacy of the ordinary Indian cannot be invaded by any government. Every Indian’s dignity is important.”
That political colour could not make it into the courtroom, though. Inside, the issue being discussed was more fundamental.
Thursday’s deliberations
On Thursday (July 20) senior advocate Arvind Datar, arguing for the petitioners, referred to a foreign article which gives 3 types of privacy. They are (1) Data privacy (2) Informational privacy and (3) Decisional privacy.
Justice DY Chandrachud asked: “What will happen if violation of privacy is by non state actor? It imposes on the state to have a regulatory framework to enforce these rights even if they are violated by a private party. The state cannot say that your right is violated by a private party and hence we are not concerned.”
Senior advocate Anand Grover then stared his argument for another petitioner. He said: “The Constitution is a living body and if it is a living body then it has to evolve. Fundamental rights have to be expanded and cannot be curtailed. India has ratified the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) which enumerates rights to privacy. States have an obligation to respect that is government must not violate the rights.
“The UN commission has two bodies. One is the General Assembly and another is the Human Rights Council. India, having ratified the resolution of international human rights, it is the obligation of the state to respect the treaty and also to protect the right of privacy as stipulated in Article 17 of the international law,” he said. “The obligation of the state is to enact legislation to protect privacy. The International Human Rights Commission has given two reports, the latest being of 2014.”
He stated that the General Assembly of UN recognises the law of privacy. “Privacy is required to protect other rights. The report of the office of the UN High Commissioner for HRs on the right to privacy in the digital age (dated 30 June 2014) lays down the contours on the right to privacy under Article 17 of the ICCPR. Article 51 and art 253 of Constitution of India requires India to give effect to international treaties.
“No person shall be deprived of his life and liberty except procedure established by law,” said Grover. He quoted the Nalsa Case, the judgment in which stated: “In the absence of a contrary legislation, municipal courts in India would respect the rules of international law.”
So, he argued, “FRs including but not limited to Art 14, 19, 21 etc have to be interpreted in line with Art 17 of ICCPR.”
Justice DY Chandrachud asked till how far can a person remain anonymous? “If any person says I don’t want to disclose the names of my parents in the birth certificate and while making his passport? What is meant by legitimate and illegitimate use of data? The state can use data of HIV affected person to provide health services. It cannot be said that under the right of privacy, it cannot not be used if it is an absolute right.”
Senior advocate Sajan Poovayya, also for a petitioner, said: “The postulated issue of recognition of the right to privacy as a fundamental right is not merely to be looked at from the viewpoint of judicial dicta but also from how Parliament has manifested it’s understanding of the said right. Even in pre-constitutional legislation the sacrosanct position of a right to privacy had been recognised insofar as social procedures had been established in such laws to create any curb or fetter on any aspect of the said right to privacy.
“In post constitutional statutes, similar procedures established by law have always been provided to create fetter on aspects of privacy. The SC in context of right to information act 2005, ordered that right to privacy is not only recognized as a basic human right to under art 12 of UDHR but parliament has recognized it under Art 21.”
Poovayya added: “Keeping pace with sociological developments through judicial pronouncements of this court, has been that the right to privacy is (a) a fundamental right and (b) deals with persons and not merely places.”
Senior advocate Meenakshi Arora, also for one of petitioners, said: “Privacy did not emerge one fine day fully formed and structured from the theoretical penumbras of various constitutional articles. Rather it is an amorphous and a protean concept that emerges from values and principles that have evolved from case law over hundreds of years.
“In England, eavesdropping was criminalised under the Justices of Peace Act 1361. In his seminal ‘Commentaries on the Laws of England’ (8th edition, 1778, volume IV, p. 167,168), Blackstone writes of common nuisances which he states are such inconvenient or troublesome offences, as annoy the whole community in general, and not merely some particular person; and are indictable only… In this category he includes, ‘6. Eaves-droppers, or such as listen under walls or windows, or the eaves of a house, to hearken after recourse, and thereupon to frame slanderous and mischievous tales, are a common nuisance and presentable at the court-leet; or are indictable at the sessions, and punishable by fine and finding sureties for their good behaviour.”
“Nowadays privacy rights are explicitly recognised or are recognised by implication under the Universal declaration of Human Rights (1948) (arguably part of customary international law and therefore part of the law of India), the International Covenant of Civil and Political Rights (ratified by India and so to be read into the Constitution), the European Convention of Human Rights, the Constitutions of the United States, the United Kingdom and virtually every other democratic or liberal Constitution. Constitutional courts in India have explicitly recognised a right to privacy for over 40 years. Our statutes recognise privacy interests as well. In particular the Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993 is relevant.
“Privacy or the right to be left alone has the following, amongst other important components:
- Privacy of one’s home and residence:
- Privacy of personal belongings and freedom from arbitrary searches and seizures:
- Privacy of personal data, and freedom from surveillance:
- Privacy of personal choice:
“The stray observations in the judgment in MP Sharma about the lack of a right of privacy were inaccurate as being somewhat overbroad in 1954 and are clearly erroneous today. As such, this Hon’ble Court may clarify the same and limit the ratio of the judgments to the facts of that case.”
The matter will be further heard on Tuesday (July 25).[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]

 Latest world news10 hours ago
Latest world news10 hours ago
 Latest world news10 hours ago
Latest world news10 hours ago
 India News10 hours ago
India News10 hours ago
 Latest world news10 hours ago
Latest world news10 hours ago
 India News9 hours ago
India News9 hours ago















