Latest business news
Fact-checking the budget: some false claims, some shortcomings, esp the ‘dole’ to farmers

[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Seen as an ‘election budget’ by all, including the upbeat members of government and the ruling BJP, the Budget 2019 with provisions that goes well beyond the ‘interim’ period of the three-month remaining term of this dispensation was found wanting by analysts with regard to some facts and promises.
As for the much flaunted sops for the poor and farmers, a look at the provisions made revealed them to be misleading and meaningless. The ‘smart’ move with regard to farmers is that the payment for Rs.6,000 annual income will start retrospectively from December 2018, and the first instalment of Rs.2,000 will be deposited in farmers’ account this March: just in time for 2019 Lok Sabha election.
The allocation for MGNREGA, about which the initial claim of an increase was followed by silence, is Rs. 60,000 crore.
This is 1.8% lower than the Rs 61,084 crore (revised estimate) allocated for 2018-19.
In February 2018, the Union budget had earmarked Rs 55,000 crore to the demand-driven rural employment scheme. In January 2019, the government had to allocate an additional Rs 6,084 crore to the programme to meet its financial demands, thus taking up the total amount to be spent in the financial year 2018-19 to Rs 61,084 crore.
For the last few years, though the demand for MGNREGA has been steadily increasing, the government has not been able to address it fully, leading to pending liabilities.
Prior to the presentation of the 2018 full budget, NREGA Sangharsh Morcha, a country-wide coalition of organisations and individuals, had submitted a memorandum to the Union finance ministry stating that there should be an annual allocation in the range of Rs 80,000 crore to be able to minimally function as per its legal provisions.
A shortfall would aggravate problems of implementation and pending liabilities, leaving the poor short-changed.
PM Kisan Samman Nidhi
Narendra Modi government’s income support scheme for small farmers – those cultivating up to two hectares of land – is Rs.6,000 a year, or Rs 500 per month. Considering a household size of five, this is 1/8th the rural poverty line of Rs 816 per person per month.
The allocation of Rs.20,000 crore in the interim budget (out of the total Rs.75,000 crore) falls short of meeting even this target. According to 2015-16 Agriculture Census, the small and marginal holdings taken together (0.00-2.00 ha) constituted 86.21% of total 14.6 crore operational holdings in the country, or a total of over 12.58 crore. If Rs. 2000/- is allocated for each small & marginal farm household as part of 1st instalment, then the total spending (cost) under PM Kisan Samman Nidhi would be 25,160 crore.
But the interim budget has allocated only Rs. 20,000 crore for 2018-19 (R.E.). So, even if landless farmers, SC-ST farmers, women farmers, sharecroppers and tenant farmers are kept aside, not all the small and marginal households can get covered under the income support scheme (assuming that 1 household operates one holding

Agriculture and food policy expert Devinder Sharma who has been advocating a fixed annual income for farmers was surprised at the figures allocated for the purpose. “How can they seriously think that a support of Rs 500 per month will help farmers out of the terrible agrarian crisis. And how will it help reduce the number of farmers suicides.”
The announcement is also discriminatory in nature. The measure is meant for small farmers with less than two hectares of land and does not take into account the 40% tenant farmers and agricultural workers who had been left out of the Budget altogether. The forest rights being demanded by the Adivasis and tribals has not even been acknowledged.
Ashok Gulati, chair professor for agriculture at ICRIER, writing in The Indian Express, said that the direct income support to farmers of total Rs..75,000 crore is nowhere near the annual loss of about Rs 2,65,000 crore that farmers have been suffering in recent years because of the low prices they have received due to restrictive marketing and trade policies. “Until major marketing reforms are initiated, there is no hope of doubling farmers’ real incomes by 2022-23,” he wrote.
Moreover, the budget has nothing to create jobs. Gulati said: “It is more like using band-aid where surgery was required.”
Apart from the shortcomings in these two of the major announcements, several of the claims of Interim Finance Minister Piyush Goyal were contested by FactChecker.in of The Spending and Policy Research Foundation which verifies the claims made by those in public life and has been certified by the International Fact-Checking Network, a unit of the Poynter Institute.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY)
Claim: 1.53 crore (15.3 million) houses constructed.
Fact: As of December 2018, at least 3.65 million houses were constructed under PMAY, according to government data. Of these, 1.25 million were constructed in urban areas whereas 2.4 million in rural areas.
Foreign Direct Investment
Claim: India could attract massive amount of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) during the last five years- as much as $239 billion.
Fact: True. But the rate of growth of FDI inflows have declined from 25 percent in 2014-15 and 23 percent in 2015-16 to eight percent in 2016-17 and one percent in 2017-18.
Distribution of LED Bulbs
Claim: At least 143 crore (1.43 billion) bulbs distributed that will save Rs 50,000 crore.
Fact: Till date, 32.3 crore (323 million) LED bulbs have been distributed, as per official records.
Swachh Bharat Mission
Claim: Mindset change achieved.
Fact: In 2018, 40 percent households with a toilet, according to a SQUAT Survey, had at least one member who defecated in the open
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
Claim: Over one crore (10 million) youth being trained to help them earn a livelihood.
Fact: Between July 2016 to 30 November 2018, under PM’s Skill Development Programme (second edition) as many as 3.6 million or 36 percent of the target had enrolled and 3.39 million (34 percent) had been trained. In the first edition, between July 2015 to and June 2016, 1.9 million were trained, as per government data.
Also Read: No Vote on Account; Modi govt presents an election Budget ‘interim’ only in name
The first edition was severely criticised for several shortcomings including low level of placements, low quality of training and inflated training numbers.
Mobile Manufacturing Units
Claim: Under Make in India initiative, mobiles and part manufacturing companies have increased from two to 268, providing huge job opportunities.
Also Read: Opposition parties calls Interim Budget a jumla, can’t be implemented
Fact: As of August 2018, there were 127 mobile manufacturing units in the country, the government told Lok Sabha citing information provided by the Indian Cellular Association.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
Latest business news
Google restores delisted Indian apps after government intervention
Google on Saturday restored all Indian apps it had removed.

Google has started to restore all the delisted Indian mobile apps on Play Store agian, which they had removed due to a disagreement over service fees. After a discussion between company representatives and IT Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw, the decision was made, according to sources.
The step was taken in response to Vaishnaw’s strong statement in which he said that it is not allowed for apps to be removed from the Google Play Store. The minister had said, India is very clear, our policy is very clear…our startups will get the protection that they need.
Vaishnaw continued saying that he has already given Google a call. They will be speaking with the app developers who were delisted this week. This is not acceptable. The minister said this kind of delisting cannot be permitted.
Ten Indian companies’ apps were banned by Google on Friday, causing outrage in one of its fastest-growing markets. With 94% of phones running on its Android platform, Google holds a large portion of the Indian market. Popular names like Naukri and Bharatmatrimony were on the list.
The main point of contention is Google’s in-app purchase fees, which range from 11% to 26%. Indian startups have long opposed the US tech giant’s actions, believing them to be unfair.
The founder of Bharat Matrimony, Christian Matrimony, Muslim Matrimony, and Jodii, Matrimony.com, expressed shock at the matchmaking apps’ removal from the Google Play Store.
Shaadi. Com CEO Anupam Mittal described it as a dark day for India’s internet, highlighting the possible broad effects on matchmaking services. He also called Google an evil.
While, Kuku FM Co-founder Vinod Kumar Meena in a statement had said that Google was behaving like a monopoly.
Meanwhile, Google temporarily withdrew the famous Indian payments app Paytm from the Play Store in 2020, claiming a few policy infractions. Due to this decision, the founder of the company as well as the larger startup community came together to build their own app stores and file lawsuits against Google.
Latest business news
Anant Ambani says he is 100% lucky to get Radhika Merchant in his life
Anant Ambani said he was grateful to get Radhika as his life partner. He said he is 100% lucky to get Radhika Merchant in his life. He said every day he is falling more and more in love with her. He added although he had known Radhika for the last 7 years, it felt he had met her only yesterday. He thanked Radhika for everything.

Anant Ambani and Radhika Merchant’s grand three-day wedding celebrations began with a glamorous cocktail night on Friday in Jamnagar. During the celebrations, Anant Ambani also gave a speech wherein he thanked his late grandfather Dhirubhai Ambani and grandmother Kokilaben Ambani for inspiring him. Anant Ambani said he was grateful to get Radhika as his life partner. He said he is 100% lucky to get Radhika Merchant in his life. He said every day he is falling more and more in love with her.
He expressed his gratitude to his mother for pulling together the lavish three-day wedding celebrations in Jamnagar. Anant thanked his mother for all she had done. He said all the arrangements had been done by his mother and nobody else. He added his mother had gone all out and she had worked 18-19 hours a day and he was extremely grateful to her.
He also thanked all the guests who were present there at the pre-wedding celebrations. He said everyone had made it to Jamnagar to make him and Radhika feel special. He said both of them were honored and humbled to have all of them present there. Anant said he was sorry if they had caused an inconvenience to anyone. He asked for forgiveness. He hoped everyone is going to enjoy the coming three days. He also thanked his mother, father, sister, brother, his sister-law and his brother in-law for making this event memorable.
Anant said everyone has been sleeping for less than 3 hours a day for the last 2-3 months and he was very happy to share this joy with everyone. The youngest Ambani talked about his personal struggles and how his parents had always supported him. He further added his life had not been entirely a bed of roses. He said he had also experienced the pain of thorns. He said he had faced many health crises.
Latest business news
Facebook chief Mark Zuckerberg shares pictures from 2nd day of Anant Ambani and Radhika Merchant pre-wedding celebrations
Zuckerberg shared pictures from the 2nd day of Anant Ambani and Radhika Merchant’s pre-wedding celebrations. In the photograph Mark Zuckerberg can be seen along with his wife Priscilla Chan. The couple is exuding happiness as they prepare for the event. He captioned the picture it is getting wild out here.
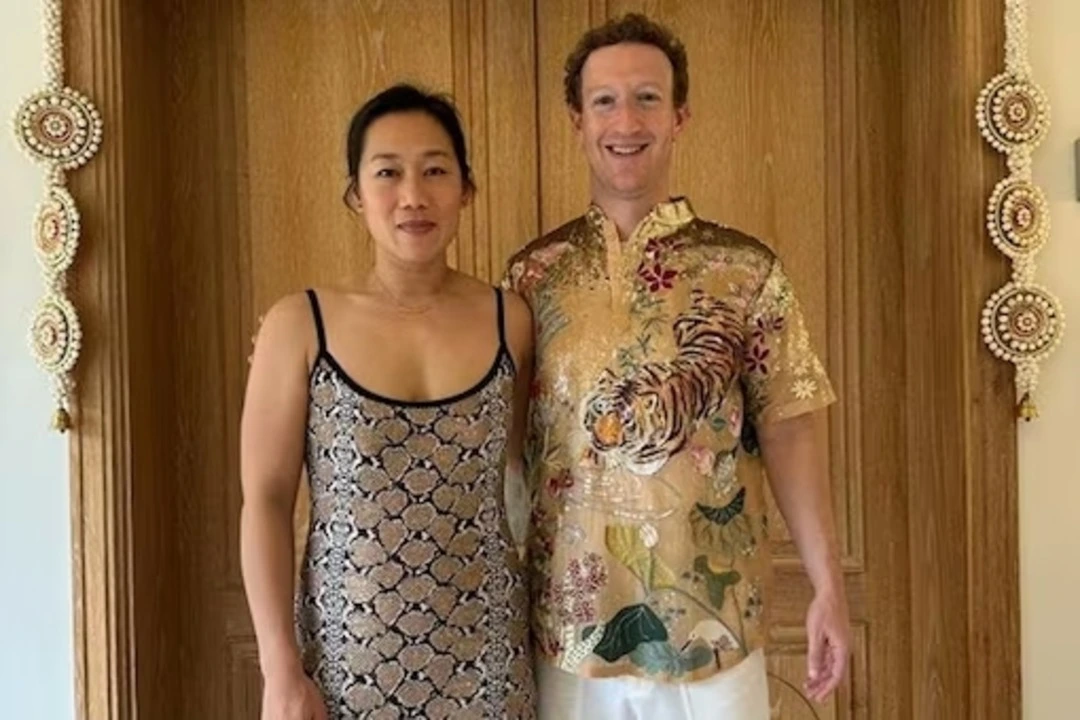

Facebook boss Mark Zuckerberg and wife Priscilla Chan joined the star- studded pre-wedding celebrations of Anant Ambani and Radhika Merchant in Jamnagar on Friday. The event was attended by many prominent figures from different fields. Zuckerberg took to his Instagram handle congratulated the couple and said he loved Indian weddings.
Zuckerberg shared pictures from the 2nd day of Anant Ambani and Radhika Merchant’s pre-wedding celebrations. In the photograph Mark Zuckerberg can be seen along with his wife Priscilla Chan. The couple is exuding happiness as they prepare for the event. He captioned the picture it is getting wild out here.
The theme of the opening day of the pre-wedding celebrations was Evening in Everland as the guests wore cocktail attire. The first day of the grand celebrations elevated the expectations of the guests for the following days. The theme of the 2nd day of the pre-wedding bash is known as a Walk on the Wildside and the guests can be seen in Jungle Fever attire.
Zuckerberg has opted for an animal print shirt with white trousers, Chan is complementing his look in a strappy one piece in black and golden. The Jungle theme is aligned to Vantara, Reliance’s animal welfare initiative undertaken and launched by Anant Ambani a few days back.
International pop star Rihana electrified the pre wedding celebrations on Friday with an amazing performance, marking her debut appearance in India. The chart topping artist engaged the audience with performances of her iconic hits which included Pour it Up, Work and Diamonds.
Zuckerberg graced the opening day, wearing a black-on-black firefly blazer and shoes from Alexander McQueen while his wife Priscilla wore a black gown with gold flower details and other accessories such as dainty chain bracelet, gold necklace and stud earrings. Mark Zuckerberg and wife Priscilla Chan are one of the Power couples invited from the global business community for the festivities currently underway at Jamnagar.
-

 2024 Lok Sabha Elections17 hours ago
2024 Lok Sabha Elections17 hours agoPM Modi votes at a polling booth in Gandhinagar Lok Sabha seat, urges people to ensure record turnout
-

 2024 Lok Sabha Elections16 hours ago
2024 Lok Sabha Elections16 hours agoMallikarjun Kharge casts vote in Kalaburagi, Karnataka
-

 Cricket news15 hours ago
Cricket news15 hours agoKKR’s Kolkata-bound flight diverted twice due to bad weather, team spends night in Varanasi
-

 2024 Lok Sabha Elections14 hours ago
2024 Lok Sabha Elections14 hours agoFormer Congress leader Radhika Khera joins BJP days after quitting over harassment
-

 Entertainment11 hours ago
Entertainment11 hours agoJolly LLB 3: Akshay Kumar, Arshad Warsi starrer lands in legal trouble, accused of disrespecting judiciary
-

 2024 Lok Sabha Elections14 hours ago
2024 Lok Sabha Elections14 hours agoPM Modi addresses rally in Khargone, urges people to choose between vote jihad or the establishment of Ram Rajya
-

 2024 Lok Sabha Elections13 hours ago
2024 Lok Sabha Elections13 hours agoAround 60.19% voter turnout till 5pm, Assam records highest voter turnout of 74.86%
-

 India News16 hours ago
India News16 hours agoSalman Khan firing case: Mumbai Crime Branch arrests fifth accused