Latest Science News
Indian scientists make surprise discovery: nanosheets can be chemical reagents too
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
By Dinesh C Sharma
Experimenting with extremely tiny materials – a millionth of a human hair’s breadth – is allowing scientists to create new materials and think of innovative applications for them. A group of Indian scientists has developed a nanosheet which can also act like a chemical reducing agent. The discovery can have potential applications in energy storage devices and next generation sensors.
The research team at the Indian Institute of Technology, Gandhinagar, has found that boron-rich nanosheets, developed by them earlier this year, can also act as a chemical reagent.
During experiments, researchers noticed that boron nanosheets could remain afloat in water for long durations. The nanosheets, they found, were remaining afloat due to hydride groups borrowed from water. This observation led them to a new idea – using nanosheets in place of sodium borohydride, a popular reagent used to chemically reduce gold salt. When gold salt was introduced in dispersion of boron-rich nanosheets, it instantly reduced and formed gold nanoparticles onto nanosheets without the need of any external help.
They found that this can be extended to synthesize platinum and silver nanoparticles by dipping nanosheets in their respective salt solutions. This means boron-rich nanosheets can function as nanoscale factories to manufacture nanoparticles by using metal ions as raw material.
“The formation of nanohybrids with gold and graphene provides the proof of concept that the inherent reducing character of these nanosheets can be availed to create diverse mixed-dimensional heterostructures in solution,” researchers observed in their study in journal Nanoscale, published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. “Our initial experiments indicate that the noble metal nanoparticle-nanosheet hybrids are excellent electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction.”
Dr. Kabeer Jasuja, who led the research team, said “this is the first example of a nanosheet that is also a reducing agent, and presents a new perspective on the chemistry of nanosheets. Our work suggests that we can now design a wide range of boron-based nanohybrids in test tube. We have shown this capability by preparing a borophene-graphene like interface in solution. The concurrence of reducing nature and planarity makes these nanosheets an intriguing alternative over conventional reducing agents.”
“In essence, we have tamed down the otherwise reactive reducing agent borohydride by virtue of nanosheets. This means that now we have an access to a mild reducing agent for selective reduction of electron rich organic moieties. This research has the potential to open up new avenues in organic synthesis that will be crucial for pharmaceutical and polymer industries,” added Dr. Arnab Dutta, a member of the research team.
The work was supported by seed funding from IIT Gandhinagar, INSPIRE Faculty Award Research Grant, and Core research Grant from the Department of Science and Technology. The team included Asha Liza James, Shikha Khandelwal, Dr. Arnab Dutta and Dr. Kabeer Jasuja. (India Science Wire)[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
India News
President Droupadi Murmu launches India’s first homegrown CAR T-cell therapy for cancer treatment
The gene-based therapy, which is developed by the IIT Bombay and Tata Memorial Centre, is being rolled out in India at about one-tenth of its price outside the country.
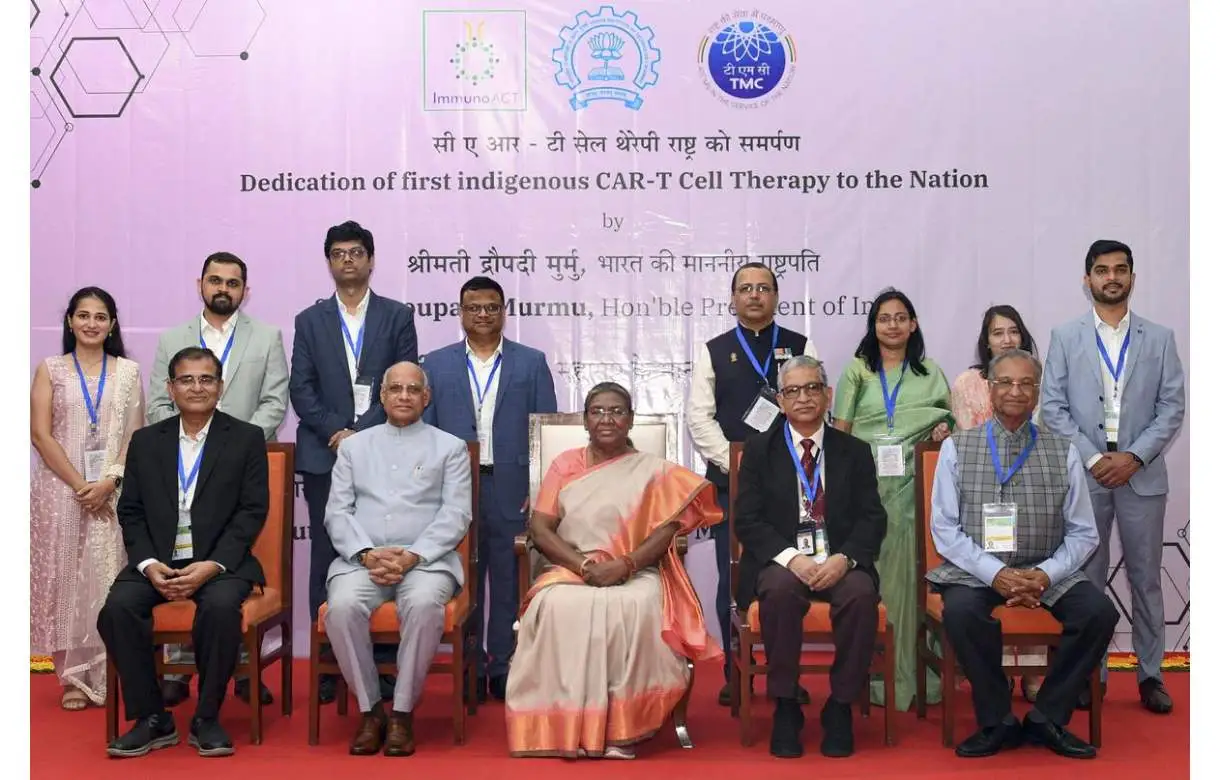

President Droupadi Murmu on Thursday launched India’s first indigenously-developed CAR T-cell therapy, a gene-based therapy, for cancer treatment, hailing it as a breakthrough that provides new hope for humankind in the battle against the diseases.
Speaking at the launch event at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay, Murmu said the indigenous development of the CAR T-cell therapy was an example of the Make in India initiative.
The gene-based therapy, which is developed by the IIT Bombay and Tata Memorial Centre, is being rolled out in India at about one-tenth of its price outside the country, as per the senior official.
In CAR T-cell therapy, a patient’s T-cells, which is a type of immune system cell or stem cell, are modified in the laboratory and inserted back into the patient to attack and destroy cancer cells after editing the stem cell.
The NexCAR19 CAR T-cell therapy, the country’s first Made in India CAR T-cell therapy, is expected to bring down the cost of treatment significantly.
During her speech, Murmu said that this therapy is considered a phenomenal advance in medical sciences. The development of this therapy is also an example of the Make in India initiative and speaks volumes about Indian scientists and physicians, she added.
The launch of India’s first gene therapy is a significant breakthrough in the battle against cancer. As this line of treatment, named CAR T-cell therapy, is accessible and affordable, it provides a new hope for the whole of humankind, President Murmu further added.
The Tata Memorial Centre director Sudeep Gupta said the CAR T-cell therapy was enormously expensive and out of the reach of an overwhelming majority of people.
Asserting that, he said NexCar19 needs to be custom manufactured for every patient under the most stringent conditions, but it has been rolled out at approximately one-tenth of the price at which it is available outside India.
The treatment costs approximately Rs 4 crore abroad against Rs 30 lakh in India, said IIT Bombay director Prof Subhasis Chaudhuri.
He further said that the low-cost CAR T-cell therapy was a huge achievement for the country and cancer patients, and places India firmly on the global map of cell and gene therapy.
Comparing the achievement of Chandrayaan-3 with CAR T-cell therapy, Chaudhuri asserted that CAR-T cell therapy heralds India’s entry into the cell and genetic engineering group.
The Tata Memorial Centre director Gupta said the treatment will help some 20,000 Indians every year, and its rollout is a milestone in the field of cancer care and genetic engineering.
He added the CAR T-cell was not only a scientific achievement of the highest order but also had immense practical application. NexCAR19 will save many, many lives and wipe many, many tears, he emphasised.
India News
ISRO launches weather satellite INSAT-3DS to monitor Earth’s surface, oceans
The Naughty Boy has now become a mature, obedient and disciplined boy like PSLV, and GSLV as they have become a very robust vehicle for ISRO, said Tomy Joseph.
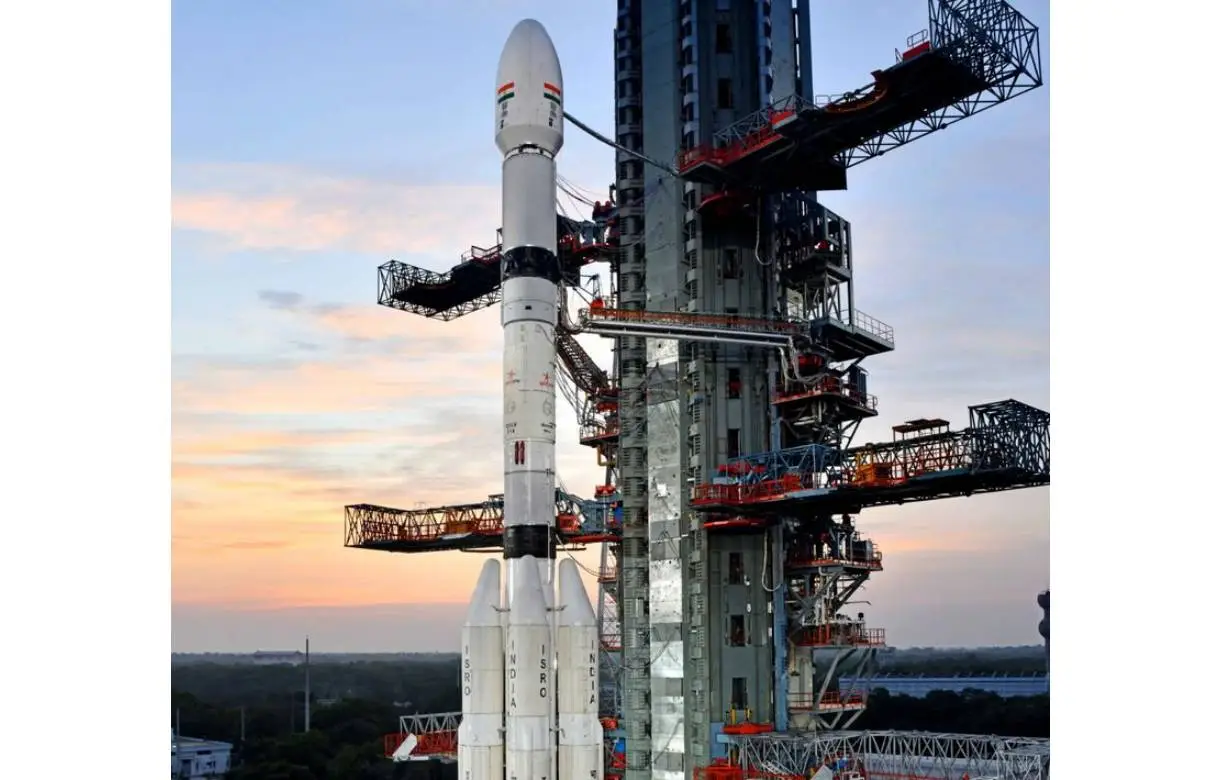

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on Saturday launched the INSAT-3DS mission from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota at 5:35 pm to monitor the Earth’s surface, observe the ocean and analyse the environment through various essential meteorological perspectives.
In its mission, the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) aimed to deploy the INSAT-3DS meteorological satellite into the Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO). Subsequent orbit-raising maneuvers will ensure that the satellite is positioned in a Geo-stationary Orbit.
After being positioned in GSO, it will provide information on diverse atmospheric conditions via vertical profiles. INSAT-3DS will manage data collection and dissemination from Data Collection Platforms (DCPs). The satellite will help in search and rescue services.
Congratulating the team, ISRO Chairman S Somanath expressed his happiness over the successful accomplishment of the mission GSLV-F14 INSAT-3DS. He further said that the spacecraft has been injected into a very good orbit. The space agency has also noted that the vehicle has performed very well.
The INSAT-3DS Mission Director, Tomy Joseph sarcastically remarked, saying the Naughty Boy has now become a mature, obedient and disciplined boy like PSLV, and GSLV as they have become a very robust vehicle for ISRO.
The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) is a launch vehicle with a length of 51.7 meters and a liftoff mass of 420 tonnes. It consists of three stages, the first stage (GS1) is made up of a solid propellant motor with 139-ton propellant and four earth-storable propellant stages (L40) strapons. Each strapon carries 40 tons of liquid propellant.
The second stage (GS2) is also an earth-storable propellant stage that carries 40-ton propellant, and the third stage (GS3) is a cryogenic stage with a 15-ton propellant loading of liquid oxygen (LOX) and liquid hydrogen (LH2).
To protect the satellite during the atmospheric regime, it is covered by an Ogive payload fairing. The GSLV is versatile and can be used to launch various spacecraft capable of performing communications, navigation, earth resource surveys, and other proprietary missions.
The launch of INSAT-3DS was a follow-on mission of Third Generation Meteorological Satellite from Geostationary Orbit. According to ISRO, the GSLV-F14/INSAT-3DS mission has been fully funded by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) and designed for enhanced meteorological observations and monitoring of land and ocean surfaces for weather forecasting and disaster warning.
The satellite will augment the Meteorological services along with the presently operational INSAT-3D and INSAT-3DR satellites.
Notably, the services will be used by various departments of the MoES such as the India Meteorology Department (IMD), National Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasting (NCMRWF), Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Indian National Center for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) and various other agencies.
India News
PM Modi says day not far when an Indian will land on moon in indigenously built spacecraft
PM Modi said a strong roadmap has been drawn till 2040 for the space sector. He made the announcement after flagging off the first Namo Bharat train on the 17 km stretch of the Delhi-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit system.
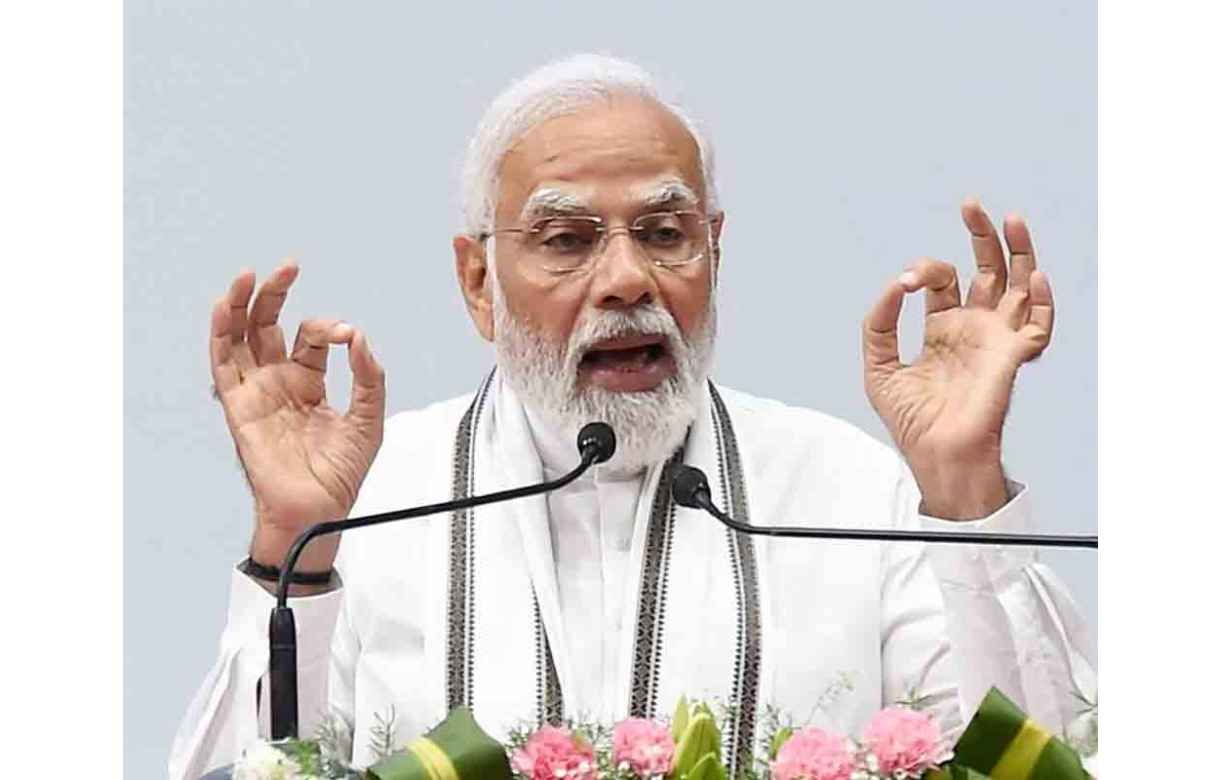

Prime minister Narendra Modi on Friday said the government has drawn up a roadmap for the development of space sector and the day is not far when an Indian will travel to the moon in an indigenously built spacecraft. PM Modi said India’s Gaganyaan will soon take Indian astronauts to space and the India wants to establish its own space station.
PM Modi said a strong roadmap has been drawn till 2040 for the space sector. He made the announcement after flagging off the first Namo Bharat train on the 17 km stretch of the Delhi-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit system.
PM Modi recalled the success of India’s moon mission Chandrayaan3 which had recently placed the country’s tricolour on the lunar surface. He said India of the 21st century is writing new chapters of progress and development for the landing on the moon has left the world awestruck.
PM Modi added with impeccable hosting of the G20 summit, today’s India has become the centre of attraction and curiosity for the world. He said today’s India wins more than 100 medals in the Asian Games.
PM Modi added today’s India launches 5G on its own strength and takes it to all corners of India. He further added todays India does the highest number of digital transactions. He said the Namo trains that were flagged off today were all made in India.
PM Modi set goals for the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) by asking engineers and scientists to work towards setting up an Indian space staion by 2035 and sending an Indian astronaut to the lunar surface by 2040. PM Modi also asked the scientists to undertake interplanetary missions like the Venus orbiter and also attempt a landing on Mars. PM Modi further added the government has handed over festival gifts by reducing the gas cylinder price by Rs 500 for Ujjwala Yojana beneficiaries.
-

 2024 Lok Sabha Elections24 hours ago
2024 Lok Sabha Elections24 hours agoDeserted by key supporters, the Kamal Nath story looks set to wind to an end in Chhindwara
-

 2024 Lok Sabha Elections22 hours ago
2024 Lok Sabha Elections22 hours agoLok Sabha Elections: Voter turnout 62.02% in Tamil Nadu till 5pm
-

 Featured24 hours ago
Featured24 hours agoNima Sulaiman joins HiLITE Group Board, her father gifts her a Porsche
-

 Cricket news6 hours ago
Cricket news6 hours agoIPL 2024: Lucknow Super Giants beat Chennai Super Kings by 8 wickets
-

 Trending23 hours ago
Trending23 hours agoRanveer Singh reacts to his viral deepfake video promoting political party
-

 2024 Lok Sabha Elections5 hours ago
2024 Lok Sabha Elections5 hours agoPrime Minister Narendra Modi takes dig at Rahul Gandhi, says like Amethi, Congress will lose its ground from Wayanad also
-

 India News1 hour ago
India News1 hour agoAAP leader Saurabh Bharadwaj says a conspiracy is underway for slow death of Arvind Kejriwal
-

 2024 Lok Sabha Elections4 hours ago
2024 Lok Sabha Elections4 hours agoRJD leader Tejashwi Yadav says BJP’s 400 paar film has become a super flop on the first day itself