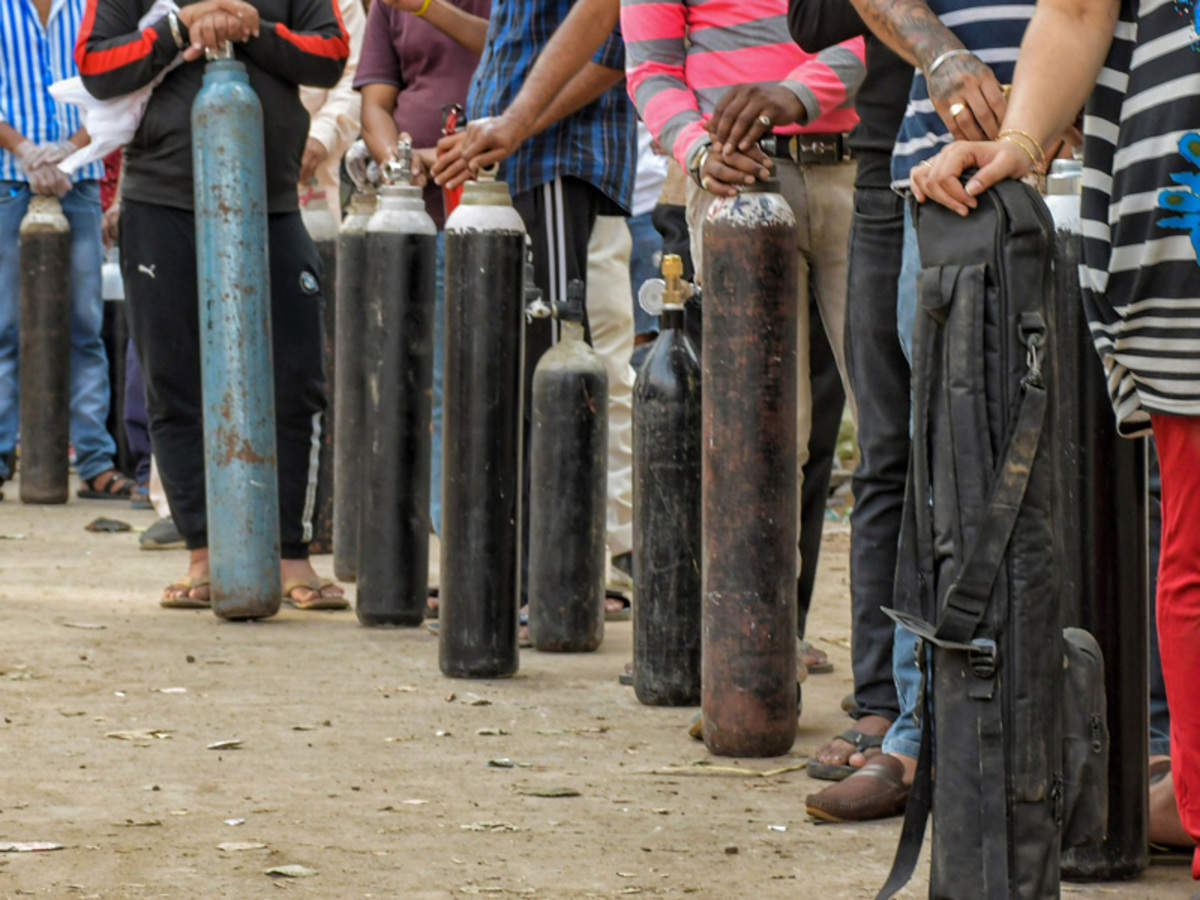
As India touches 34 lakh active Covid-19 infections, a number of states have reported shortages of medical oxygen for an increasing number of patients in need of oxygen support. The last two weeks have seen innumerable private hospitals, those that have been bywords for medical expertise like Batra Hospital, St Stephens’ Hospital, Ganga Ram all queue up to the Delhi High Court with their complaints that they don’t have oxygen at all. And if they did, they would run out i a few hours. The issue is so grave now that after the deaths without oxygen at Ganga Ram, Batra Hospital and now in Karanataka’s Chamarajnagar, it is not looking like solutions have been kept ready. Here’s our primer.
Is Delhi running out of oxygen in hospitals?
Delhi has been suffering from oxygen shortage and the deficit of supply of oxygen killed 12 people on Saturday and 25 last week. The Arvind Kejriwal government has asked for around 970 metric tonnes of oxygen per day. The centre, however, has only allotted 590 MT (increased from 490 MT on Saturday). The Supreme Court has directed the Centre to ensure that the deficit in the supply of oxygen to the GNCTD shall be rectified on or before the midnight of 3 May 2021.
What about Maharashtra oxygen needs?
Consumption of medical oxygen in Maharashtra has reached the state’s full production capacity of 1,250 tonnes. The state has 6,68,353 active cases of Covid-19 infections, and about 10% of them an estimated 60,000-65,000 — are on oxygen support, the highest for any state.
The state on Sunday reported 56,647 fresh coronavirus positive cases and 669 fatalities, taking the tally of infections to 47,22,401 and the toll to 70,284, the state health department said. Maharashtra is additionally taking 50 tonnes from Gujarat and another 50 tonnes from Chhattisgarh daily. It is also slated to receive 100 tonnes from Reliance’s plant in Jamnagar, Gujarat.
Madhya Pradesh oxygen requirement is growing. Why?
Madhya Pradesh reported 12,662 new COVID-19 cases on Sunday, which took its infection tally to 5,88,368, while 94 deaths pushed the fatality count to 5,812, health officials said. The state requires 250 tonnes of medical oxygen daily. The state does not have its own manufacturing plant and relies on Gujarat, Chhattisgarh, and Uttar Pradesh for oxygen supply. As cases rise in neighbouring states, MP is staring at the possibility of supplies from there running out. Gujarat’s requirement has crossed 500 tonnes per day for over 49,737 active Covid-19 cases.
How many people have died in Rajasthan due to oxygen shortage?
Rajasthan on Sunday registered 159 fatalities due to Covid-9 and a record 18,298 fresh cases, taking the death toll to 4,558 and the infection count to 6,33,951, according to an official report. The number of active cases also increased to 1,89,178 from 1,82,301 a day before, the report said.
Chief minister and Congress leader Ashok Gehlot talked about battling Covid-19, He said as per the experience so far, 12% of the active patients need oxygen today. So the state need about 466 metric tonnes (MTs) of oxygen but are getting only 265 MTs and hence there is a shortage of nearly 201 MTs. Rajasthan has a share of 5% active cases in the country but oxygen allotment is only 1.6%. In a week’s time, the state would need 550 MTs of oxygen if the growth of cases continues like now. Hence, the state government has requested the Centre that 201 MTs additional oxygen be allotted to us immediately today itself. Three government ministers went to Delhi and met four senior union ministers on this too and the CM has spoken to the most important people in the country.
If people die because of oxygen shortage, it is neither in the state or the Centre’s interest as people will say their dear ones are dying while the governments are fighting. So both need to work together and not indulge in any blame game. Also, if states want to help fellow states with oxygen or medicines, that should be allowed under the Centre’s supervision.
The Centre-appointed Empowered Group-2, formed to monitor the supply of essential medical equipment during the pandemic, has been focusing on 12 high-burden states — Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Karnataka, Delhi, Kerala, Chhattisgarh, Tamil Nadu, Punjab and Haryana — where oxygen requirement is expected to increase in the coming days. Over 17,000 tonnes of oxygen will be directed in three batches from states that have surplus oxygen to these 12 states to meet their projected demand.
The problem is acute in rural areas, which are going through a rise in Covid-19 cases but have no large storage tankers, and in smaller nursing homes, which rely on daily supply of oxygen cylinders.
What about the situation in Uttar Pradesh?
The state reported 303 more COVID-19 deaths on Saturday, pushing the fatality count to 12,874. As many as 30,317 fresh cases pushed the infection tally to 12,82,504. A total of 9,67,797 people have been cured of the contagion so far. Of the fresh cases, as many as 3,125 were reported from Lucknow, 1,514 from Kanpur, 1,497 from Varanasi, 1,470 from Gautam Buddh Nagar, 1,274 from Allahabad, 1,236 from Meerut, 1,204 from Ghaziabad and 1,070 from Gorakhpur, among others.
Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath has said there is no oxygen shortage in the state, but the ground report suggests a different story. Reports suggested that 7-8 COVID-19 patients died at Paras Hospital in Agra due to acute shortage of beds and medical oxygen on April 24. On April 28, Durgawati Hospital in Barhalganj reported five deaths due to lack of oxygen as the hospital administration had to slow down the oxygen for patients and there was a delay in replenishing the stock.
A report by NDTV suggested that at least seven patients died in two Meerut hospitals – three at Anand hospital and four at KMC hospital – due to oxygen shortage.
How much oxygen is produced in India?
In the present situation, most states have diverted their entire oxygen production for medical use as India is grappling with the unprecedented second wave of Covid-19.
Industry experts said India has the capacity to produce more than 7,000 metric tonnes of medical oxygen. The major manufacturers are Inox Air Products, Linde India, Goyal MG Gases Pvt Ltd, National Oxygen Limited. The largest of these, Inox, produces 2000 tonnes per day. An Inox official said that the oxygen manufacturer is currently contributing to 60% of the total medical oxygen requirement in the country. The company has stopped nitrogen and argon gas production and diverted all resources for oxygen production, he said.
Reports said that during the first wave of the pandemic last year, smaller manufacturers of industrial oxygen were also allowed to produce medical oxygen by changing certain specifications. This has helped expand the medical oxygen production capacity.
How is oxygen manufactured? Isn’t it in the air?
Manufacturers prepare liquid oxygen with 99.5% purity, which is stored in jumbo tankers, and transported to distributors in cryogenic tankers at a specified temperature. To fill the oxygen in jumbo cylinders and dura cylinders, a process of regasification is followed to convert the it into gaseous form. These cylinders then go to smaller suppliers or directly to hospitals. An industry expert said the problem is demand is high, but there are not enough cylinders and tankers to store and transport oxygen.
Read Also: Uttar Pradesh BJP spokesperson dies of Covid-19
In the last one year, Inox started two plants in West Bengal and UP to produce 200 and 150 tonnes oxygen respectively per day. An Inox official said they have plans to install more plants in Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal, but it will not solve the immediate crisis.


 India News19 hours ago
India News19 hours ago
 Latest world news18 hours ago
Latest world news18 hours ago
 Latest world news4 hours ago
Latest world news4 hours ago
 Latest world news4 hours ago
Latest world news4 hours ago
 India News4 hours ago
India News4 hours ago
 Latest world news4 hours ago
Latest world news4 hours ago
 India News4 hours ago
India News4 hours ago