[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
- Nearly nine out of 10 Indians hold a favourable opinion of Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- Seven-in-ten Indians are now satisfied with the way things are going in the country.
- More than eight-in-ten (85%) voice trust in the national government.
- The public is also quite satisfied (79%) with the way their democracy is currently working.
These findings of a Pew Research Centre survey come as a major morale booster for the BJP ahead of some key state elections and with two years to go before the next Lok Sabha elections.
The survey was conducted just as Prime Minister Narendra Modi was going to complete three years in government, between Feb. 21 – Mar. 10, 2017, a few months after the drastic, much reviled step of demonetisation. One may quibble about the sample size of the survey, which was 2,464. It was based on face-to-face interviews with respondents in 16 of India’s 18 most populous states and Delhi.
Modi’s popularity rating in the survey is seen as unusual for a leader having completed three years in office, with no sign of his popularity waning since 2015 when his government was one year old. “Three years into Modi’s five-year tenure, the honeymoon period for his administration may be over but the public’s love affair with current conditions in India is even more intense,” Pew said.
For those who oppose Modi for being autocratic, the survey provides a reality check: A majority, 53% support military rule and 55% of Indians back a governing system in which a strong leader can make decisions without interference from parliament or the courts. Support for autocratic rule is higher in India than in any other nation surveyed. India is one of only four nations where half or more of the public supports governing by the military.
The Pew research findings also lend credence to views about the saffron party’s ‘intolerance’: BJP supporters in general had more intense and stronger views that those of other parties.
About eight-in-ten (79%) in India are satisfied with the way their democracy is currently working.
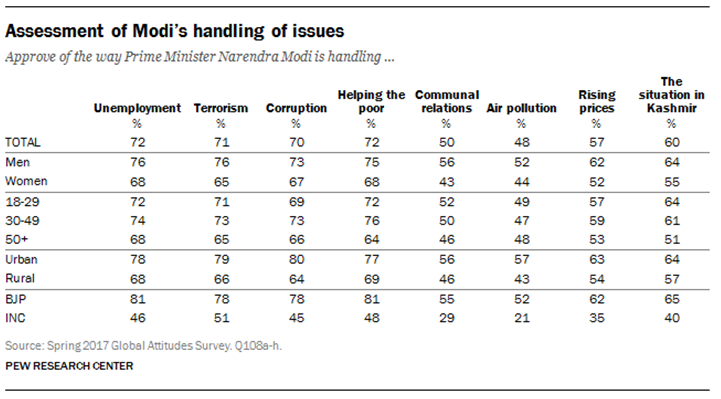
Modi’s lowest ratings are for his handling of communal relations (50%) – the long fractious tensions between Muslims and Hindus and India’s various castes – and for his efforts to curb air pollution (48%). Women are particularly critical of how he has dealt with communal relations, as are people living in northern India. Rural Indians are less supportive than those in urban areas of his handling of both communal relations and air pollution. But both of these issues are relatively low priorities for Indian adults.
The Pew survey found that 88 per cent of Indians held a favourable view of Modi, a shade higher than the 87 per cent who gave him a thumbs-up in 2015, a year after he swept to power promising to transform India into a high-growth economy.
Modi’s favourable rating is 31 percentage points higher than that of Congress president Sonia Gandhi, the leader of the main opposition Congress party, 30 points more than that for her son and Congress vice-president Rahul Gandhi, who is expected to take over the party leadership, and 49 percent higher than Delhi chief minister and AAP convenor Arvind Kejriwal.
Public backing for Arvind Kejriwal has consistently dipped after coming to power in Delhi in 2015. Two years on, only 39 per cent Indians view him in a favourable light.
Not just Modi, but also his party, the BJP, continues to enjoy widespread public support. More than eight-in-ten Indians have a favourable view of the party, roughly its level of backing for the past three years, says the report.
About six-in-ten Indians express a positive opinion of the Congress party. Again, this is fairly consistent with past support. But the gap between BJP and Congress backing, which was 26 points in 2015 and then narrowed to 13 points in 2016, has now widened again to 25 points.
Indians in rural areas (63%) are more supportive of Congress than those in cities (51%). Those with a primary education or less are more likely to back Congress than are those with at least some college education.
Notably, 60% of Congress party supporters have a favourable view of the BJP. Just 45% of BJP backers hold a positive opinion of the Congress party. Neither party’s supporters hold positive views of the AAP.
While there has been much criticism of Modi government over demonetisation and growing unemployment, the poll found that more than 80 percent of those surveyed said economic conditions were good, up 19 percentage points since just before the 2014 election. “Overall, seven-in-ten Indians are now satisfied with the way things are going in the country. This positive assessment of India’s direction has nearly doubled since 2014,” Pew said.
More than 83 per cent Indians say the nation’s economy is good, and 30 per cent say it is very good.
Bloomberg reported that in an email reply, Bruce Stokes of Pew Research said that the data on hand does not include public sentiment over the last few months after signs emerged that the economy was in a funk after two economic disruptions in 6 months – demonetisation and the GST roll out. “What is important is that satisfaction with the economy was widely shared across demographic groups. And trust in the government and satisfaction with democracy was correlated with economic satisfaction,” Stokes told Bloomberg.
Roughly three-quarters of the public (76%) says the media, such as television, radio, newspapers and online news, have a good influence on the way things are going in India. But such sentiment is far less intensely felt (39% very good) and is down 16 points from public views in 2015. BJP supporters (79%) are much more likely than Congress backers (59%) to say the media have a good influence, and Congress supporters are somewhat more likely to have no view.
BJP supporters and those who live in urban areas are significantly more likely than Congress party backers and those in rural regions to support rule by a strong leader, by the military and by experts. Rural respondents and Congress supporters are significantly more likely to offer no opinion, however. Those with some college education or more are significantly more likely than those with a primary education or less to back rule by experts, although those with less education are also more likely to not answer. In general, there are no major differences by gender and age.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]






















